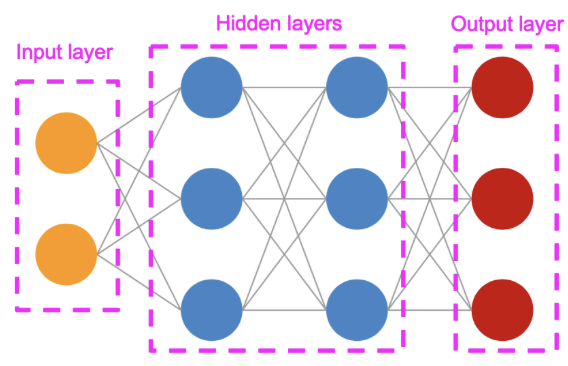
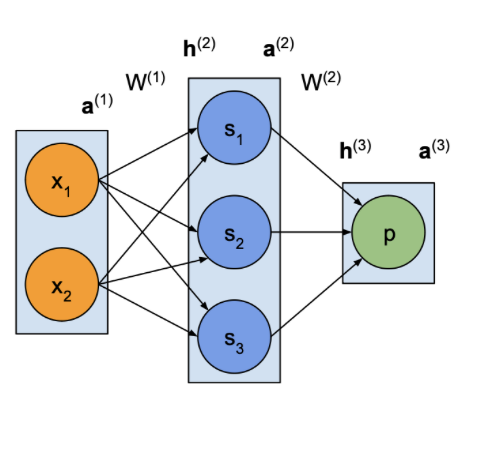
신경망
MLP
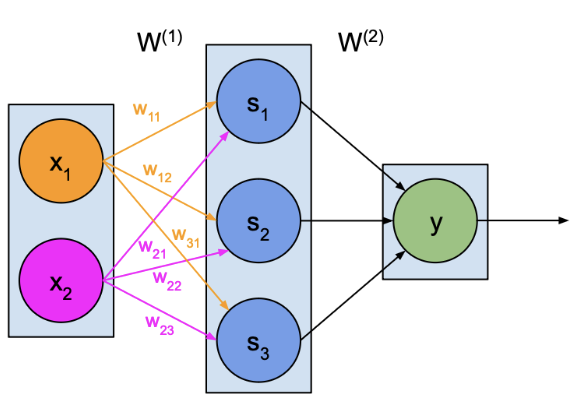
– 가중치
– 순 입력
– 활성화
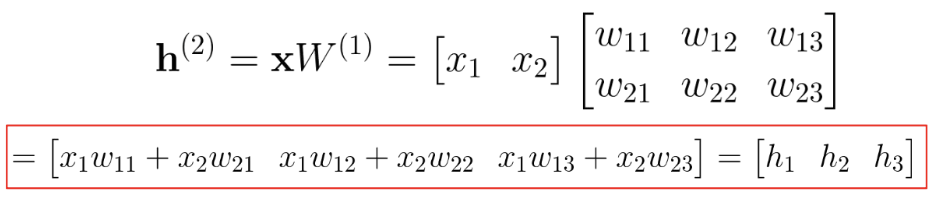
다음과 같이 벡터 곱으로 계산됩니다.
처음부터 NN 구현
import numpy as np
class MLP(object):
"""A Multilayer Perceptron class.
"""
def __init__(self, num_inputs=3, hidden_layers=(3, 3), num_outputs=2):
"""Constructor for the MLP. Takes the number of inputs,
a variable number of hidden layers, and number of outputs
Args:
num_inputs (int): Number of inputs
hidden_layers (list): A list of ints for the hidden layers
num_outputs (int): Number of outputs
"""
self.num_inputs = num_inputs
self.hidden_layers = hidden_layers
self.num_outputs = num_outputs
# create a generic representation of the layers
layers = (num_inputs) + hidden_layers + (num_outputs)
# create random connection weights for the layers
weights = ()
for i in range(len(layers)-1):
w = np.random.rand(layers(i), layers(i+1))
weights.append(w)
self.weights = weights
def forward_propagate(self, inputs):
"""Computes forward propagation of the network based on input signals.
Args:
inputs (ndarray): Input signals
Returns:
activations (ndarray): Output values
"""
# the input layer activation is just the input itself
activations = inputs
# iterate through the network layers
for w in self.weights:
# calculate matrix multiplication between previous activation and weight matrix
net_inputs = np.dot(activations, w)
# apply sigmoid activation function
activations = self._sigmoid(net_inputs)
# return output layer activation
return activations
def _sigmoid(self, x):
"""Sigmoid activation function
Args:
x (float): Value to be processed
Returns:
y (float): Output
"""
y = 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return y
if __name__ == "__main__":
# create a Multilayer Perceptron
mlp = MLP()
# set random values for network's input
inputs = np.random.rand(mlp.num_inputs)
# perform forward propagation
output = mlp.forward_propagate(inputs)
print("Network activation: {}".format(output))
신경망 훈련

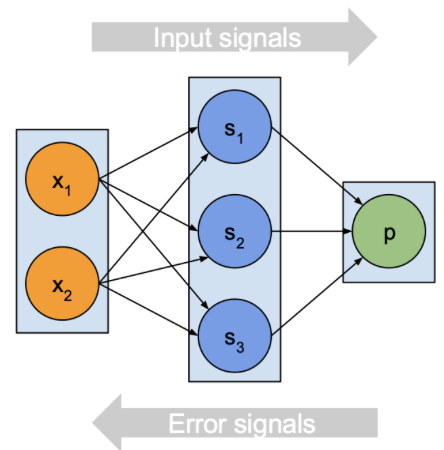
입력 신호
1. y 값 예측
2. 오류 계산
오류 신호
1. 기울기 계산
2. 파라미터 업데이트

위의 방정식에서와 같이 체인 규칙을 사용하여 기울기를 계산합니다.
경사도를 낮추는 방향으로 기울기 비율만큼 단계 -> 오차 최소화
신경망 교육: 처음부터 역전파 구현
import numpy as np
from random import random
class MLP(object):
"""A Multilayer Perceptron class.
"""
def __init__(self, num_inputs=3, hidden_layers=(3, 3), num_outputs=2):
"""Constructor for the MLP. Takes the number of inputs,
a variable number of hidden layers, and number of outputs
Args:
num_inputs (int): Number of inputs
hidden_layers (list): A list of ints for the hidden layers
num_outputs (int): Number of outputs
"""
self.num_inputs = num_inputs
self.hidden_layers = hidden_layers
self.num_outputs = num_outputs
# create a generic representation of the layers
layers = (num_inputs) + hidden_layers + (num_outputs)
# create random connection weights for the layers
weights = ()
for i in range(len(layers) - 1):
w = np.random.rand(layers(i), layers(i + 1))
weights.append(w)
self.weights = weights
# save derivatives per layer
derivatives = ()
for i in range(len(layers) - 1):
d = np.zeros((layers(i), layers(i + 1)))
derivatives.append(d)
self.derivatives = derivatives
# save activations per layer
activations = ()
for i in range(len(layers)):
a = np.zeros(layers(i))
activations.append(a)
self.activations = activations
def forward_propagate(self, inputs):
"""Computes forward propagation of the network based on input signals.
Args:
inputs (ndarray): Input signals
Returns:
activations (ndarray): Output values
"""
# the input layer activation is just the input itself
activations = inputs
# save the activations for backpropogation
self.activations(0) = activations
# iterate through the network layers
for i, w in enumerate(self.weights):
# calculate matrix multiplication between previous activation and weight matrix
net_inputs = np.dot(activations, w)
# apply sigmoid activation function
activations = self._sigmoid(net_inputs)
# save the activations for backpropogation
self.activations(i + 1) = activations
# return output layer activation
return activations
def back_propagate(self, error):
"""Backpropogates an error signal.
Args:
error (ndarray): The error to backprop.
Returns:
error (ndarray): The final error of the input
"""
# iterate backwards through the network layers
for i in reversed(range(len(self.derivatives))):
# get activation for previous layer
activations = self.activations(i+1)
# apply sigmoid derivative function
delta = error * self._sigmoid_derivative(activations)
# reshape delta as to have it as a 2d array
delta_re = delta.reshape(delta.shape(0), -1).T
# get activations for current layer
current_activations = self.activations(i)
# reshape activations as to have them as a 2d column matrix
current_activations = current_activations.reshape(current_activations.shape(0),-1)
# save derivative after applying matrix multiplication
self.derivatives(i) = np.dot(current_activations, delta_re)
# backpropogate the next error
error = np.dot(delta, self.weights(i).T)
def train(self, inputs, targets, epochs, learning_rate):
"""Trains model running forward prop and backprop
Args:
inputs (ndarray): X
targets (ndarray): Y
epochs (int): Num. epochs we want to train the network for
learning_rate (float): Step to apply to gradient descent
"""
# now enter the training loop
for i in range(epochs):
sum_errors = 0
# iterate through all the training data
for j, input in enumerate(inputs):
target = targets(j)
# activate the network!
output = self.forward_propagate(input)
error = target - output
self.back_propagate(error)
# now perform gradient descent on the derivatives
# (this will update the weights
self.gradient_descent(learning_rate)
# keep track of the MSE for reporting later
sum_errors += self._mse(target, output)
# Epoch complete, report the training error
print("Error: {} at epoch {}".format(sum_errors / len(items), i+1))
print("Training complete!")
print("=====")
def gradient_descent(self, learningRate=1):
"""Learns by descending the gradient
Args:
learningRate (float): How fast to learn.
"""
# update the weights by stepping down the gradient
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
weights = self.weights(i)
derivatives = self.derivatives(i)
weights += derivatives * learningRate
def _sigmoid(self, x):
"""Sigmoid activation function
Args:
x (float): Value to be processed
Returns:
y (float): Output
"""
y = 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return y
def _sigmoid_derivative(self, x):
"""Sigmoid derivative function
Args:
x (float): Value to be processed
Returns:
y (float): Output
"""
return x * (1.0 - x)
def _mse(self, target, output):
"""Mean Squared Error loss function
Args:
target (ndarray): The ground trut
output (ndarray): The predicted values
Returns:
(float): Output
"""
return np.average((target - output) ** 2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# create a dataset to train a network for the sum operation
items = np.array(((random()/2 for _ in range(2)) for _ in range(1000)))
targets = np.array(((i(0) + i(1)) for i in items))
# create a Multilayer Perceptron with one hidden layer
mlp = MLP(2, (5), 1)
# train network
mlp.train(items, targets, 50, 0.1)
# create dummy data
input = np.array((0.3, 0.1))
target = np.array((0.4))
# get a prediction
output = mlp.forward_propagate(input)
print()
print("Our network believes that {} + {} is equal to {}".format(input(0), input(1), output(0)))
![[Android] Access [Android] Access](https://good.eternals.kr/wp-content/plugins/contextual-related-posts/default.png)